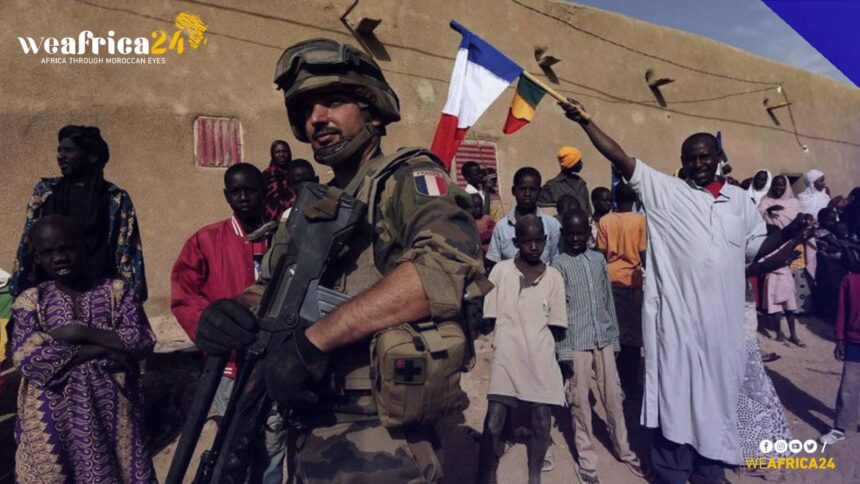
“Exploring France’s Exploitation of African Natural Resources: A Comprehensive Analysis”
Introduction:
The relationship between France and Africa has been one of the longest and most complex in modern history. France has had a significant impact on Africa, both culturally and economically. One of the most significant ways in which France has impacted Africa is through its exploitation of African natural resources. In this article, we will explore the various ways in which France has tried to gain control over the natural resources of Africa, the impact this has had on African nations, and the challenges that have arisen as a result.
French Colonialism and Natural Resource Exploitation:
The Legacy of French Colonialism
The exploitation of African natural resources by France has its roots in the colonial era. During this time, France established colonies in Africa and imposed its control over the economies and resources of these territories. French colonial rule was characterized by the exploitation of African resources for the benefit of the French economy. This exploitation was facilitated by the policies and practices of the French colonial administration, which were designed to transfer wealth from Africa to France.
The Scramble for African Resources
As European powers raced to establish colonies in Africa during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, the competition for control over African resources became increasingly intense. France was no exception and was actively involved in the “scramble for Africa.” French colonial administrators saw Africa as a source of raw materials, labor, and markets for French goods. They established policies and practices that allowed them to extract as much wealth as possible from their African colonies.
The Impact of French Colonialism on African Natural Resources
The impact of French colonial rule on African natural resources was profound. The exploitation of African resources by France had several consequences for African nations. First, it weakened African economies by depriving them of valuable resources and creating an unequal economic relationship between France and Africa. Second, it stifled economic growth in Africa by diverting resources away from development and towards exploitation. Finally, it created a legacy of dependency that continues to impact African economies today.
Post-Independence Exploitation of African Natural Resources:
The Continuation of Exploitation After Independence
The end of French colonial rule in Africa did not bring an end to the exploitation of African natural resources by France. Instead, France continued to exert control over African economies through a combination of economic policies, trade agreements, and cultural influence. French corporations and investors have continued to extract African resources, often with the support of the French government.
The Role of France in African Resource Conflicts
France’s continued involvement in the exploitation of African natural resources has often been a source of conflict in Africa. In many cases, French corporations and the French government have been accused of supporting oppressive regimes and engaging in resource-grabbing practices that have had a devastating impact on African communities. This has contributed to instability and conflict in many African nations, exacerbating poverty and inequality.
The Impact of French Resource Exploitation on African Development
The impact of French resource exploitation on African development has been significant. By draining valuable resources from African economies, French corporations, and the French government have hindered economic growth and impeded the development of African nations. This has contributed to poverty and inequality in Africa, creating a legacy of dependency that continues to impact the continent today.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, France’s exploitation of African natural resources has had a profound impact on Africa. The legacy of French colonialism and the continued exploitation of African resources by France has hindered economic growth, contributed to conflict, and created a legacy of dependency that continues to impact African nations today. While there have been efforts to address the negative impact of French resource exploitation in Africa, much work remains to be done. For African nations to achieve sustainable and equitable development, they must be able to take control of their resources and determine their economic destinies. This will require concerted efforts by African leaders, civil society organizations, and the international community to challenge the legacy of French exploitation and promote more equitable economic relationships between France and Africa.
In addition, there needs to be greater transparency and accountability in the extractive industries in Africa. This includes the development of strong regulatory frameworks and the implementation of measures to ensure that the benefits of natural resource extraction are shared equitably between African nations and the companies that are extracting their resources. Greater transparency and accountability will also help to ensure that the exploitation of African resources does not contribute to conflict and instability in the region.
Ultimately, the exploitation of African natural resources by France is a complex issue that requires a multi-faceted approach to address. It will require the recognition of the historical legacy of exploitation, the development of strong regulatory frameworks, and the promotion of more equitable economic relationships between France and Africa. By working together, we can create a future in which African nations can fully realize their economic potential and build a more prosperous and equitable world for all.
Sources:
- “France in Black Africa” by Francis Terry McNamara
- “The Scramble for Africa: White Man’s Conquest of the Dark Continent from 1876 to 1912” by Thomas Pakenham