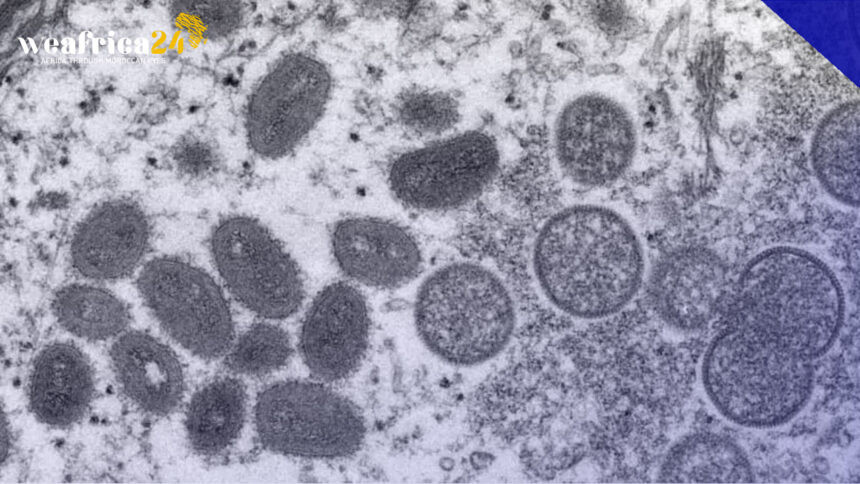
The World Health Organization (WHO) is deeply troubled by the surge in monkeypox cases in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), where the country has already reported 581 deaths out of nearly 13,000 cases. This high mortality rate is alarming, especially considering that the WHO had recently lifted its alert on this disease. While the specialized UN agency attributes this surge to structural issues, Congolese health authorities cite financial challenges.
The epidemic has affected 21 out of the DRC’s 26 provinces, with recent spikes recorded in the provinces of Equateur, Sankuru, Maï-Ndombe, and the capital city, Kinshasa. According to the WHO, the rapid spread is primarily a result of inadequate healthcare infrastructure. However, the response team highlights financial constraints as the primary hurdle.
The government struggles to allocate the necessary $4 million for an emergency plan in these four provinces, where the virus is spreading rapidly. Cris Kasita, the response coordinator, reveals, “This plan has never been implemented, and we have never responded in Kinshasa. All we are doing is routine data collection. However effective, active surveillance to combat Monkeypox has not yet begun. That’s where we are struggling. As we approach the festivities, if we don’t take action proactively, it will be challenging for Kinshasa to contain this epidemic.”
Facing the highest reported annual case count, with new infections emerging in previously unaffected regions like the capital and the provinces of Lualaba and South Kivu, the WHO deems the risk of cross-border and global spread as “high.”
The investigation traces back to March, involving a Belgian tourist’s visit to the DRC with multiple reported sexual partners.
The mode of transmission, sometimes misunderstood in the DRC due to a lack of awareness, includes human-to-human contact with skin lesions or exposure to an infected animal. However, knowledge about the virus remains limited in the region.